SUS through Examples
The SUS language enables a direct translation to a netlist, which is crucial for hardware synthesis. To illustrate this, consider simple examples.
XOR gate
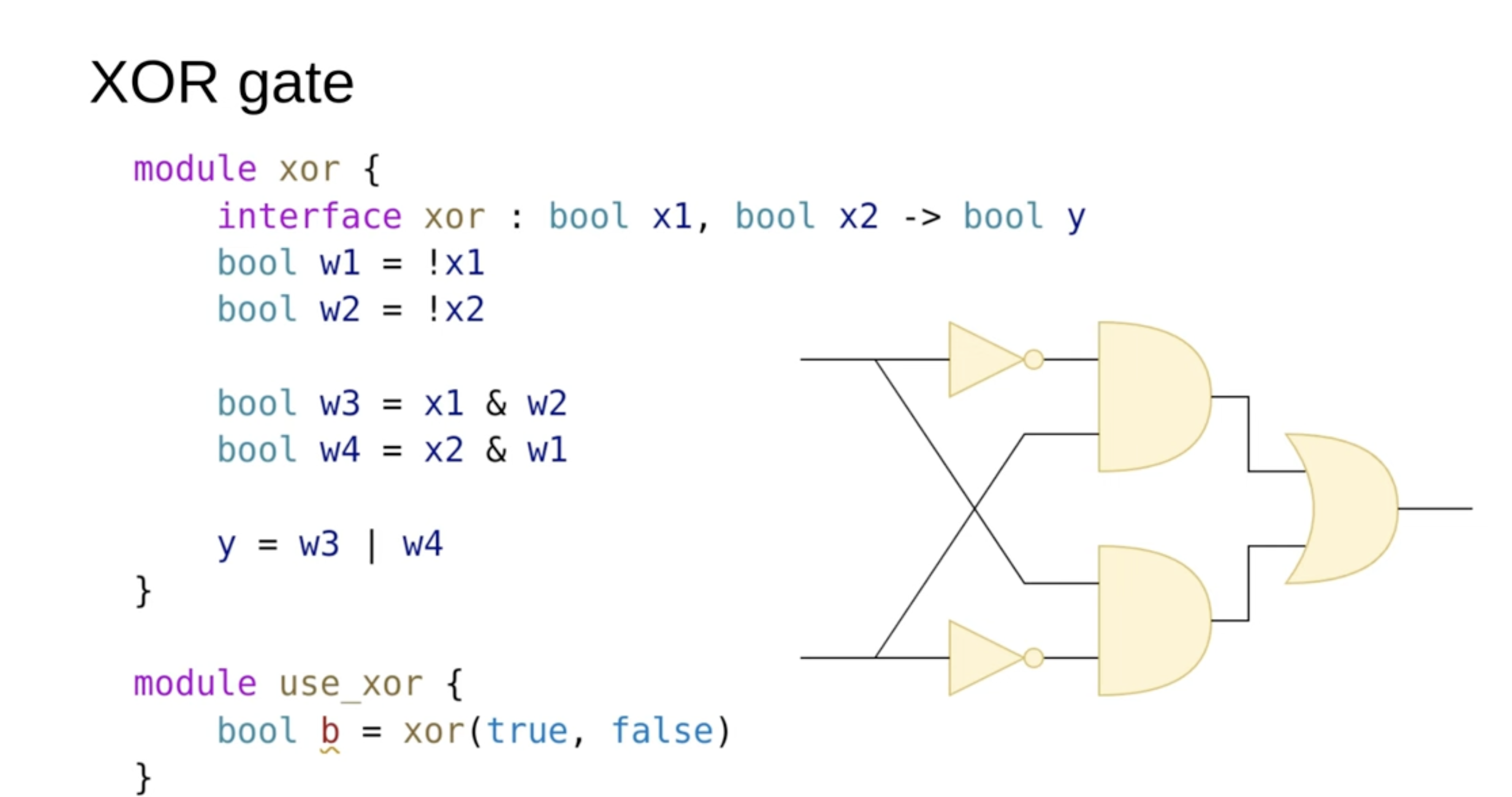
In the SUS language, this module would have two inputs, X1 and X2, and an output Y. In the middle, we may have several intermediary operators and variables that perform necessary computations, ultimately assigning the result to the output Y.
Below the module definition, you'll see how such a module can be instantiated. The instantiation follows a function-call-like syntax, which, when synthesized, translates into corresponding hardware gates in the netlist."
Conditions
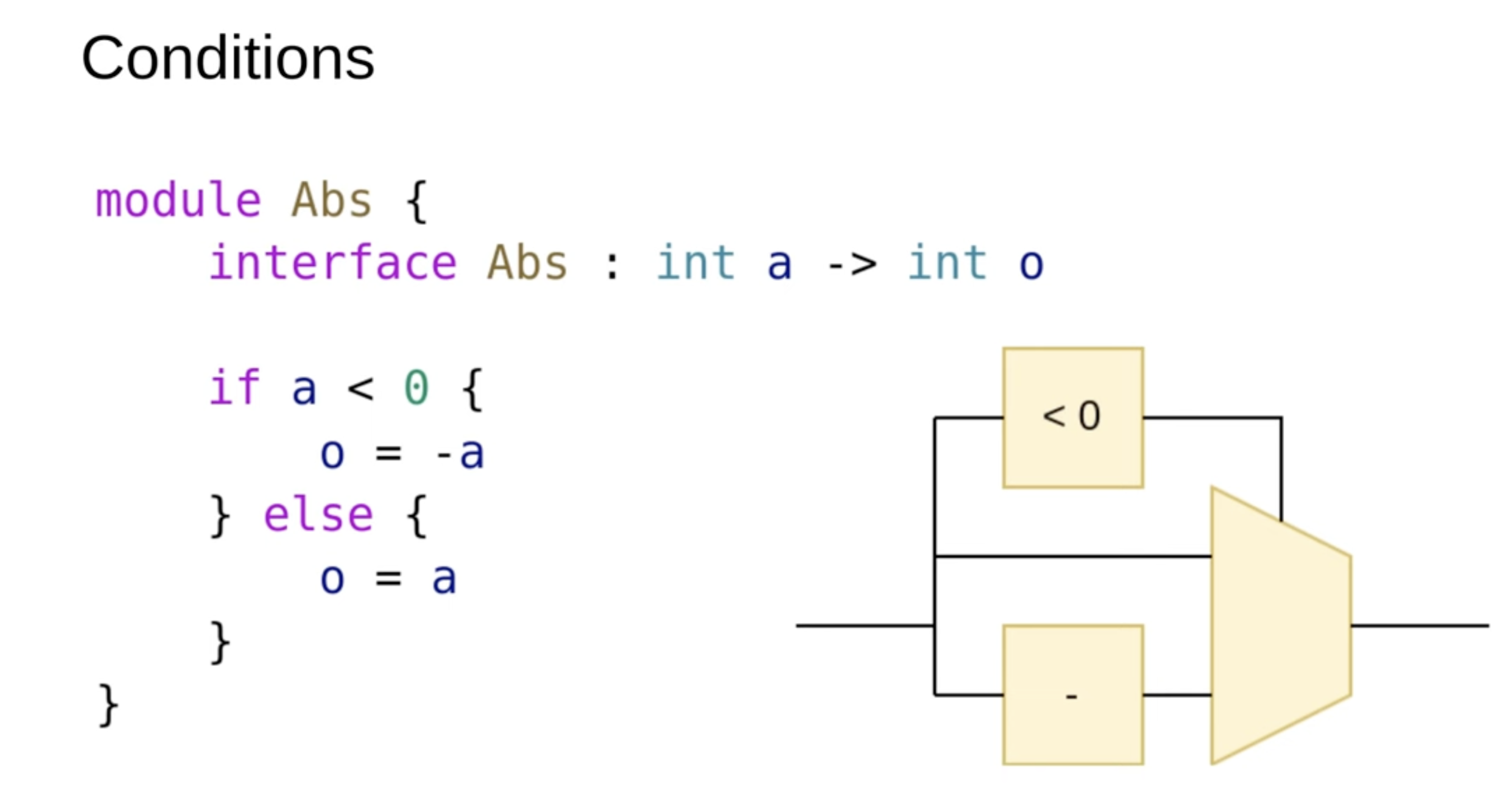
In hardware design, it's important to understand that all hardware is always running on a chip; you can't just conditionally enable or disable hardware. The only thing that changes with conditions is whether certain assignments are made. For example, in the given scenario, inputs are checked to see if they are less than zero. If they are, a negation block is used, otherwise, the value is used as-is. However, any additional hardware in the middle will still execute regardless of the conditions, as it's always running at runtime. These are essentially runtime if statements.
Multiple Interfaces
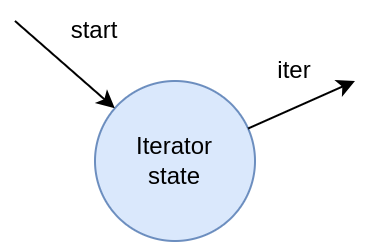

A module is presented here that implements a for-loop as a runtime iterator. This module has two interfaces: a 'start' interface, which initiates the iterator. A value is provided to define the range for iteration. Once the iteration begins, the module also features a 'trigger' interface, which acts like a callback within the hardware. This interface informs the hardware of the current values being iterated through. The implementation below demonstrates the module, including a condition and other necessary components
How to use Multiple Interfaces?
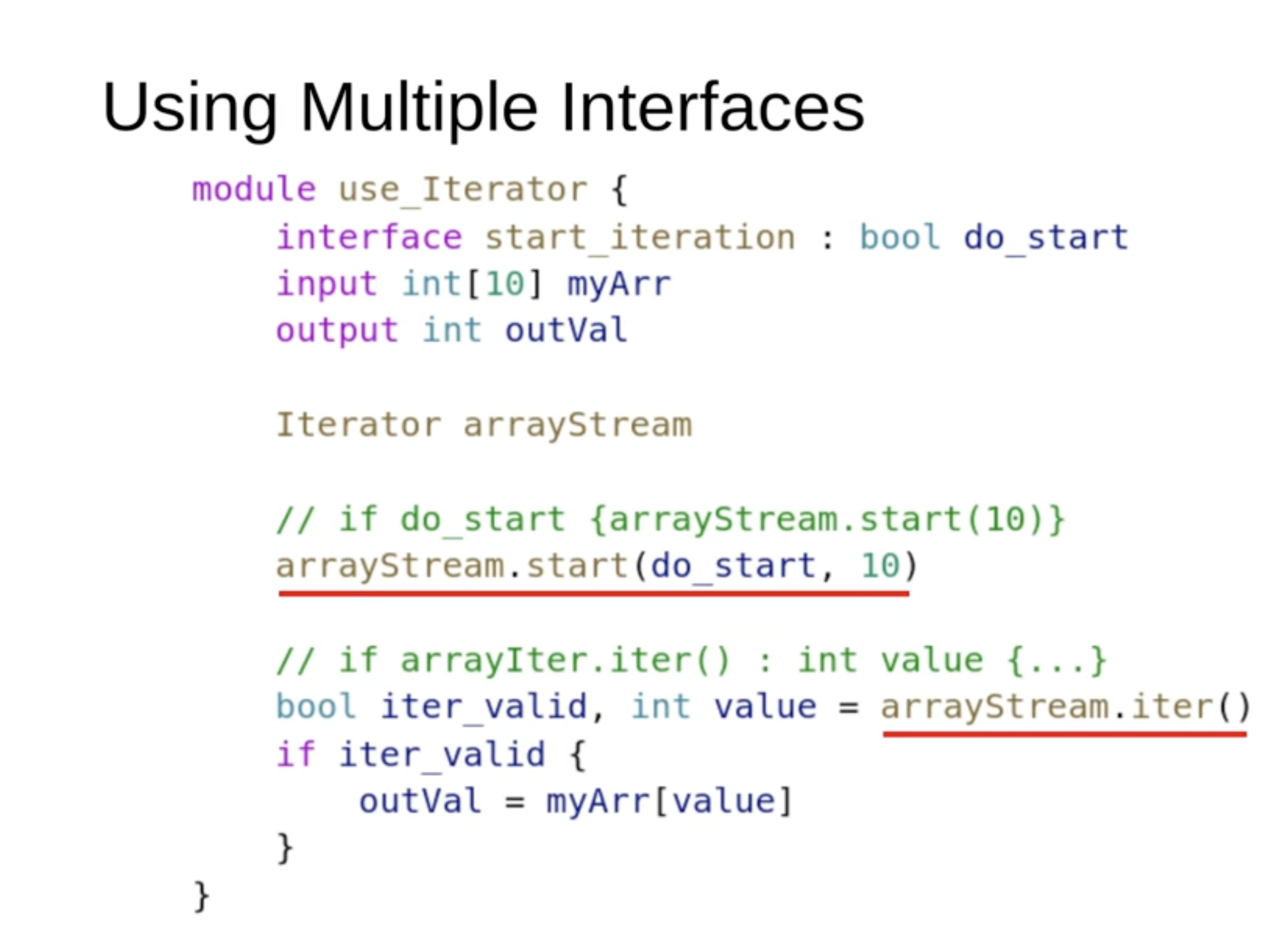
To use it, you would wrap it in an array of values, set up output values, and instantiate an iterator. You can then start iterating from a specific point and use a callback function.
FIZZ-BUZZ Lookup Table using Generative Code
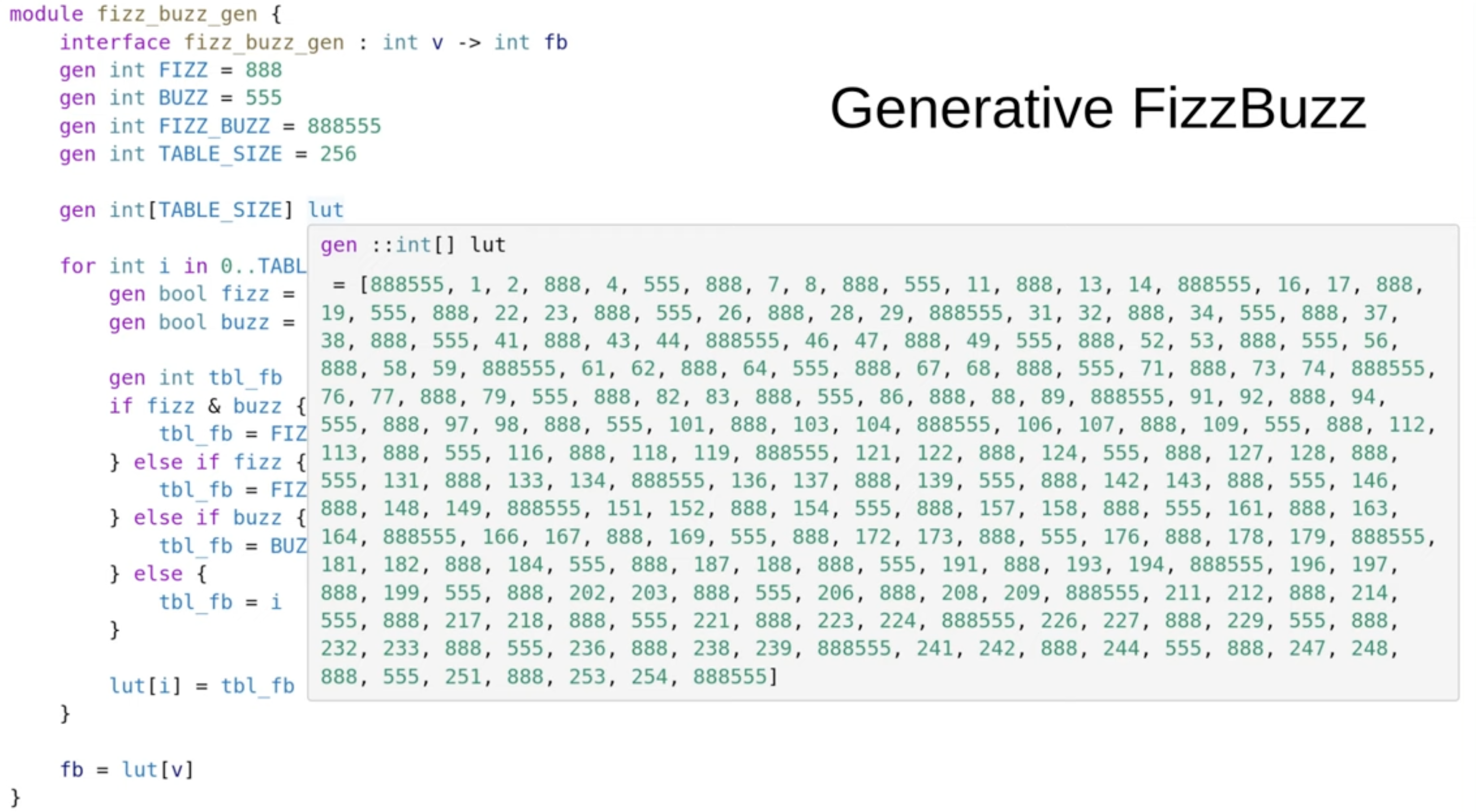
In the end, the generative code is executed and all that results is a lookup table.